
Your working capital cycle is the amount of time it takes for you to convert your net working capital amount into cash. This can be found by taking the time in between when you working capital ratio meaning have to pay your short-term debts and when you will receive outstanding accounts receivables. There are several useful metrics that can help a company avoid these pitfalls.

Current liabilities are best paid with current assets like cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities because these assets can be converted into cash much quicker than fixed assets. The faster the assets can be converted into cash, the more likely the company will have the cash in time to pay its debts. The cash flow from operating activities section aims to identify the cash impact of all assets and liabilities tied to operations, not solely current assets and liabilities. The formula to calculate the working capital ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities.
The ratio is used by lenders and creditors when deciding whether to extend credit to a borrower. Working capital is the amount of money your business https://www.bookstime.com/ needs to conduct its short-term operations. The working capital ratio is calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets.

The benefit of neglecting inventory and other non-current assets is that liquidating inventory may not be simple or desirable, so the quick ratio ignores those as a source of short-term liquidity. One common financial ratio used to measure working capital is the current ratio, a metric designed to provide a measure of a company’s liquidity risk. Note, only the operating current assets and operating current liabilities are highlighted in the screenshot, which we’ll soon elaborate on. The amount of working capital needed varies by industry, company size, and risk profile. Industries with longer production cycles require higher working capital due to slower inventory turnover. Alternatively, bigger retail companies interacting with numerous customers daily, can generate short-term funds quickly and often need lower working capital.
This type of financing does not provide physical cash to you, however, it gets you the goods you would have spent a loan on. Receiving trade credit or vendor credit can make all the difference in your cash flow. Your business can be flourishing and your working capital positive and then all of a sudden you start to face a cash flow crisis. Suddenly your working capital declines and without adequate working capital, you cannot operate your business efficiently or even expand it. These discounts may seem small but they can save you some money which can help you handle your pressing expenses and debts. The money you save from getting good deals and discounts from suppliers will help grow your working capital.
Your company should produce inventory at the level of market demand, especially if you produce perishable items to cut down on current liabilities. Improving the way you manage your inventory can help lower your working capital needs. It consists of items that you have prepared for sales, used in production, and held for sale.

The cash conversion cycle provides important information on how quickly, on average, a company turns over inventory and converts inventory into paid receivables. Working capital is the term used to describe the available money that a business has on hand in order to support all activities and operations happening in the short term. Unlike long-term investments such as fixed assets and R&D, having enough working capital is the key to running a business smoothly. As just noted, a working capital ratio of less than 1.0 is an indicator of liquidity problems, while a ratio higher than 2.0 indicates good liquidity. A low ratio can be triggered by difficult competitive conditions, poor management, or excessive bad debts.

Generally, the higher the ratio, the better an indicator of a company’s ability to pay short-term liabilities. In financial accounting, working capital is a specific subset of balance sheet items and is calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets. If a company cannot meet its financial obligations, then it is in danger of bankruptcy, no matter how rosy its prospects for future growth may be. However, the working capital ratio is not a truly accurate indication of a company’s liquidity position.

When analyzing an income statement, it’s essential to understand the income before taxes. This figure represents the company’s earnings after expenses, such as production costs and operating expenses, are deducted but before tax expenses are applied. For small businesses with few income streams, you might generate single-step income statements on a regular basis and a multi-step income statement annually.

Income statements are also carefully reviewed when a business wants to cut spending or determine strategies for growth. Cost of goods and services in an income statement denote the expenses incurred to sell the final goods. They also include the costs of materials used to develop the products and the labor needed to get the goods to market. Non-operating expenses, on the other hand, refer to costs incurred but not linked directly to the core functions of a business. Such expenses include obsolete inventory charges or even the settlement of a lawsuit.
Together with the Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement, it is included in every company’s Annual Report – the publicly available, comprehensive overview of a business’ health and financial standing. An Income Statement is a financial statement that shows the revenues and expenses of a company over a specific accounting period. Operating Income represents what’s earned from regular business operations. In other words, it’s the profit before any non-operating income, non-operating expenses, interest, or taxes are subtracted from revenues. EBIT is a term commonly used in finance and stands for Earnings Before Interest and Taxes.
The operating revenue for an auto manufacturer would be realized through the production and sale of autos. Operating revenue is generated from the core business activities of a company. This is the total amount of revenues that the entity generates in the reporting period. For example, if the entity is selling clothes, this line will show the total amount of clothes that the entity sells in monetary during the months, quarters, or annually.
The Treasury Solicitor has three years to disclaim, which is reduced to one year on receipt of a specific request to disclaim from a member of the public. However, there is a risk that some property held by the Crown’s Nominee could give rise to third party claims. This risk arises primarily from un-disclaimed land, but the current which accounts are found in an income statement legal view is that such claims, if identifiable, would not succeed and, therefore, no liability has been recognised. Payments to kin can include interest from which Income Tax is deducted and paid directly to His Majesty’s Revenue and Customs. The Crown’s Nominee holds information for the cases handled in relation to bona vacantia.
Comparing these figures over time will reveal any growth or decline in the company’s revenue-generating ability. FreshBooks provides free template income statements that are pre-formatted for your needs. All you need to do is fill in the empty fields with the numbers you’ve calculated.

It is also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, where profit or loss is determined by subtracting all expenses from the revenues of a company. In their eyes, money you save with the help of an accountant—by reducing your tax burden, or helping you pay lower interest on debt—is separate from money you save by operating your business day-to-day. Any money saved in that way will impact your income tax and interest payments—neither of which are included when calculating operating income. A lot of business owners focus their attention on the bottom line—their net profit. There’s only so much you can do to improve your bottom line by cutting expenses. At some point, you’ll hit a ceiling, and the only way to grow the bottom line is to grow your revenue.

If total revenue minus total operating expenses is a negative number, this is considered an operating loss. To understand the above formula with some real numbers, let’s assume that a fictitious sports merchandise business, which additionally provides training, is reporting its income statement for a recent hypothetical quarter. Once the income before taxes is determined, the next step is to consider the tax expenses. This value is the company’s tax obligation on the income earned during the specified period. A multi-step income statement calculates net income and separates operational income from non-operational income—giving you a more complete picture of where your business stands.
While the Income Statement shows profitability, the Balance Sheet shows financial position, and the Cash Flow Statement shows how the company generates and uses cash. Investors may use income statements, along with other financial statements, to make investing decisions and determine the financial health of a company. The cash flow statement reconciles the income statement with the balance sheet in three major business activities. The balance sheet provides an overview of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific time and date.
If, based on the work I have performed, I conclude that there is a material misstatement of this other information, I am required to report that fact. In auditing the financial statements, I have concluded that the Crown’s Nominee’s use of the going concern basis of accounting in the preparation of the financial statements is appropriate. The financial reporting framework that has been applied in the preparation of the financial statements is applicable law and UK-adopted International Accounting Standards. It often only has information for a specific period of time, called a “statement period.” Typically a statement is one month long, but sometimes it could be once per quarter. A balance sheet helps investors and analysts to understand a company’s financial health. This statement accurately depicts the financial position of a company at a specific time, typically the end of a fiscal quarter or year.
Overall, when it is difficult or not economically feasible to track the costs of a product individually, process costing is typically the best cost system to use. Why have three different cost calculation methods for process costing, and why use one version instead of another? The different calculations are required for different cost accounting needs. Alternatively, process costing that is based on standard costs is required for costing systems that use standard costs. In general, the simplest costing approach is the weighted average method, with FIFO costing being the most difficult.

Process Costing is the cost accounting method in which production overhead is equally allocated to each product due to their similarity and mass production. The company assumes that each product requires the same overhead cost. Moreover, raw material needs to pass through multiple stages of production before turning into finished goods. And it is very complicated to assign the overhead cost individual unit.
Costs are assigned to products, usually in a large batch, which might include an entire month’s production. Eventually, costs have to be allocated to individual units of product. It assigns average costs to each unit, and is the opposite extreme of Job costing which attempts to measure individual costs of production of each unit. It is a method of assigning costs to units of production in companies producing large quantities of homogeneous products. Process costing is a method of costing used mainly in manufacturing where units are continuously mass-produced through one or more processes. Examples of this include the manufacture of erasers, chemicals or processed food.In process costing it is the process that is costed (unlike job costing where each job is costed separately).
This makes it easy to switch over to a job costing system from a process costing one if the need arises, or to adopt a hybrid approach that uses portions of both systems. This process costing method is the most complicated process costing method compared to the weighted average and standard cost methods. In a situation whereby costs change significantly from one period to the next, the FIFO method can be used to get a more precise product costing.
We are going to discuss how these methods are used in a process costing system but first let’s have an understanding of what a process costing system is. The similarities between job order cost systems and process cost systems are the product costs of materials, labor, and overhead, which are used determine the cost per unit, and the inventory values. Job order costing and process costing are the accounting systems used to record the costs expended to produce a product. Conversion costs are the direct labor and manufacturing overhead involved in the production process and exist regardless of the accounting system used.

This results in the costing system selected being the one that best matches the manufacturing process. Process costing is the only reasonable approach to determining product costs in https://www.bookstime.com/articles/process-costing many industries. It uses most of the same journal entries found in a job costing environment, so there is no need to restructure the chart of accounts to any significant degree.

For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. The articles and research support materials process costing available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.

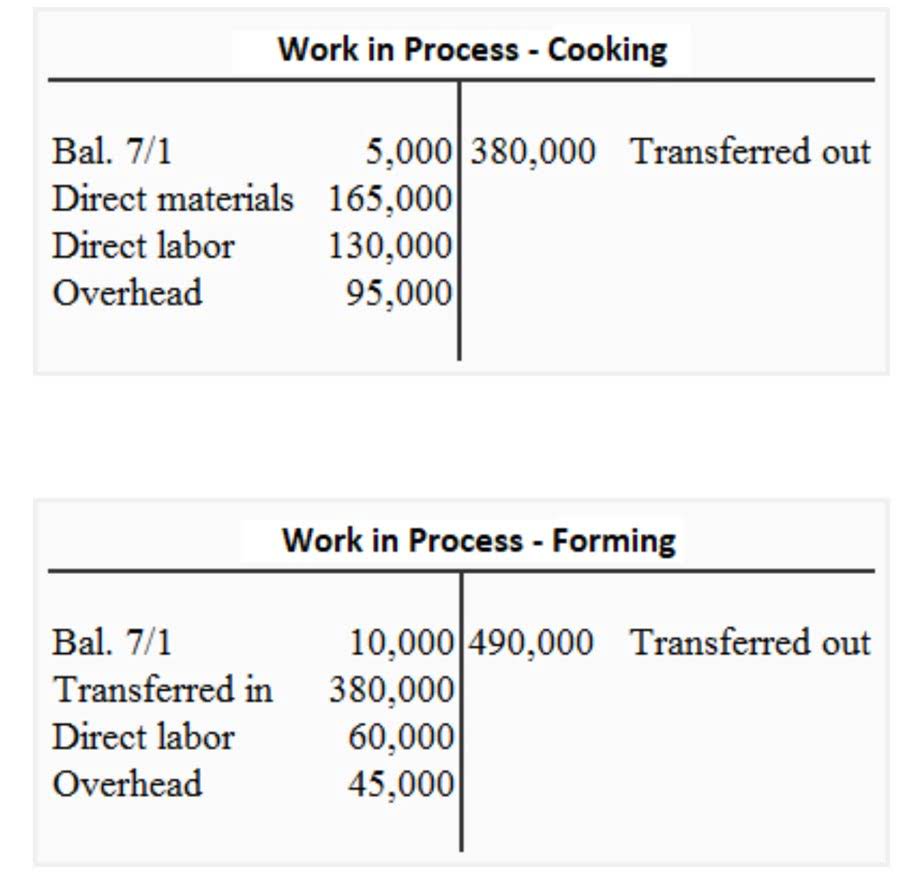
Ore is introduced in the melting stage, alloys in the skimming stage, etc. (this is equally true for labor and overhead). This necessitates the employment of a separate Work in Process account for each major manufacturing activity. Examine the graphic below that compares job and process costing, noting in particular the difference in how costs are shifted out of work in process. Process costing entails handing off accumulated costs from one department to the next. Process costing is a type of operation costing which is used to ascertain the cost of a product at each process or stage of manufacture. A process can be referred to as the sub-unit of an organization specifically defined for cost collection purpose.
That is, the production and processing of products begin in the Mixing Department. Each Department inputs direct materials and further processes the products. Then the Packaging Department transfers the products to Finished Goods Inventory. The sticks are dried, and then sent to the packaging department, where the sticks are embossed with the Rock City Percussion logo, inspected, paired, packaged, and shipped to retail outlets such as Guitar Center. Examples of the industries where this type of production occurs include oil refining, food production, and chemical processing. For example, how would you determine the precise cost required to create one gallon of aviation fuel, when thousands of gallons of the same fuel are gushing out of a refinery every hour?
The cost allocated per unit is recorded on the balance sheet in the inventory asset account. Then, when the products are eventually sold, the cost is shifted to the cost of goods sold account on the income statement. Company ABC is manufacturing which specializes in shoe production, they mainly focus on the local market. The production needs to go through multiple processes which they called the departments.